Chapter 12 NCBI: The National Center for Biotechnology Information
NOTE: The following material was partially adapted by N. Brouwer from Wikipedia. See the underlying .Rmd file for information on specific paragraphs from Wikipedia.
12.1 Key concepts
- NCBI
- Rentrez
- accession numbers
- BLAST
12.2 NCBI
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It was founded in 1988 and is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to the basic and applied life sciences and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine.
In this chapter we’ll briefly discuss the major databases, following up with specific details in subsequent chapters. One thing to note is that in practice people do no always adhere to the specific names of databases and other tools. For example, someone may say “I searched NCBI for sequences.” It would be more accurate to say “I used Entrez to search GenBank for sequences.” For in-depth details on all the features see Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information
12.3 GenBank sequence database
The GenBank sequence database is an open access collection of publicly available DNA and protein sequences. If you’ve work with sequence data, you’ll work with GenBank. GenBank is the actual database, and it can be searched several ways. For example, you can search for a sequence by its ID number (accession number) if you know it, or do a BLAST search using an actual sequence to look for similar sequences.
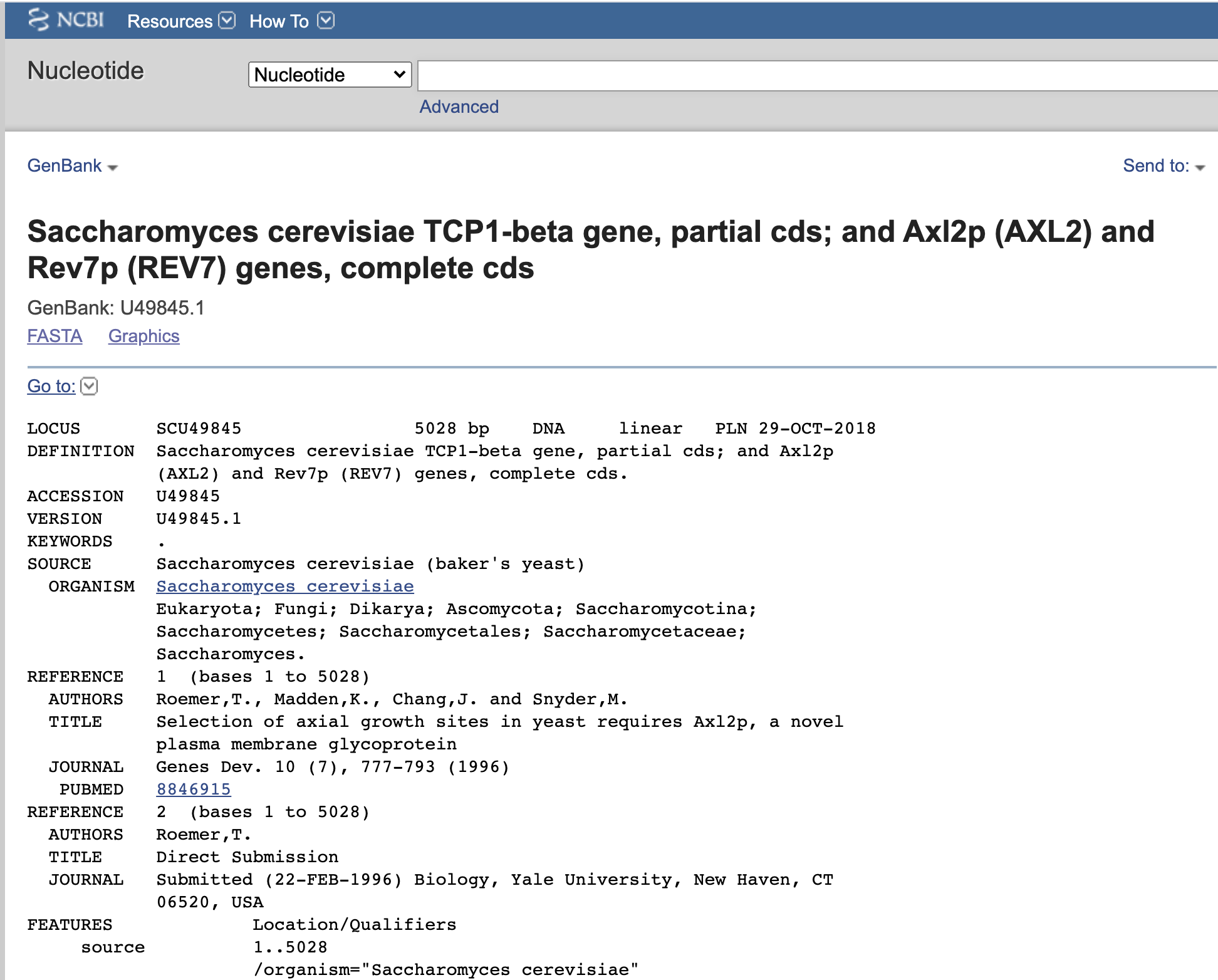
A key component of GenBank are the GeneBank Records, which are annotated summaries of sequences in the databases. For example, below is shown record for a gene pallysin https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AAC65720 from syphilis In addition to the actual A, T, C, and Gs of the sequences, the record provides metadata, such as the scientific name of the organism (Treponema pallidum), who did the sequencing, the name of the paper where the sequence was published, and important features of the gene.
A key feature of PubMed records is that they are hyperlinked to other NCBI databases. For example, you can click link under the name of the paper which reported the sequence of the gene and it will take you to the PubMed record for that paper (see below). You can also click the “Run BLAST” link and you can search the database for similar sequences. This protein coded for by this particular gene has had its structured solved using x-ray crystallography, and you can see these results under “Protein 3D Structure.” In a later chapter we’ll get to know these records in further detail.
12.4 PubMed and PubMed Central article database
PubMed and PubMed Central (PMC) are databases of scientific articles related to data contained in NCBI databases. PubMed contains basic bibliographic information, the abstract, relevant links to sequences, and to the websites of the actual publishers of the papers. If the text of an article is open-access, PMC should have a copy of it. Articles in PMC contain relevant hyperlinks, such as to any sequences that are mentioned. For example, the image below show where the sequence of Tp0751 is mentioned in a paper and linked to the GenBank record we looked at above.
12.5 Entrez
Entrez is a search engine and web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases of the NCBI website. The name “Entrez” (a greeting meaning “Come in” in French) was chosen to reflect the spirit of welcoming the public to search the content available from NCBI.
Entrez Global Query is an integrated search and retrieval system that provides access to all databases simultaneously with a single query and user interface. Entrez can efficiently retrieve related sequences, structures, and references. The Entrez system can provide views of gene and protein sequences and chromosome maps. Some textbooks are also available online through the Entrez system.
12.6 BLAST
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence (called a query) with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence.